verilog HDL basics
Verilog Language
基于HDLbits
Basics
bitwise and logical
bitwise-NOT (
~) and logical-NOT (!)Bitwise-NOT (
~)- Operation: The bitwise-NOT operator performs a bitwise inversion on its operand. This means that each bit of the operand is flipped;
0becomes1and1becomes0. - Usage: It is used when you need to invert the bits of a binary number or a vector.
Logical-NOT (
!)- Operation: The logical-NOT operator evaluates the logical value of its operand. It converts
0to1and any non-zero value to0. - Usage: It is used when you want to negate a condition or expression. This is typically used in control flow statements like
iforwhile.
- Operation: The bitwise-NOT operator performs a bitwise inversion on its operand. This means that each bit of the operand is flipped;
bitwise-AND (
&) and logical-AND (&&)
Norgate
1 | module top_module( |
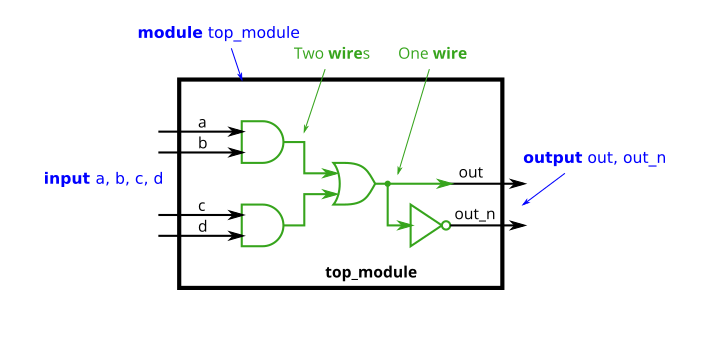
Xnorgate
1 | module top_module( |
Wire decl
1 |
|
7458
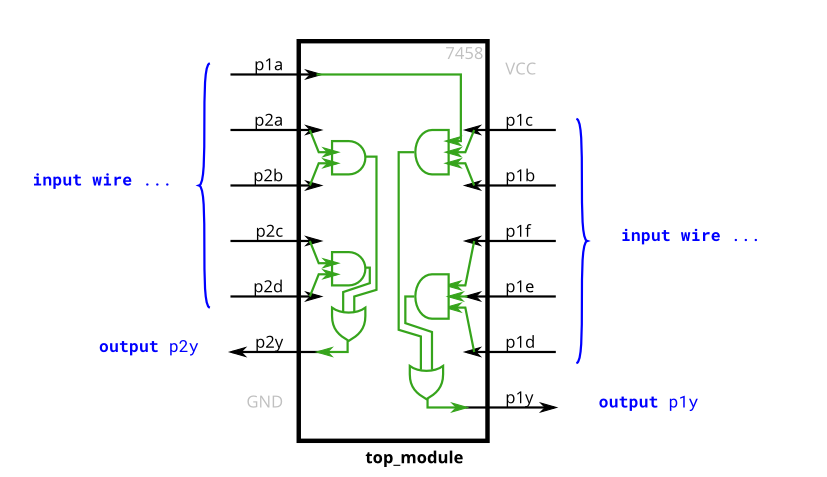
1 | module top_module ( |
Vectors
Vector 0
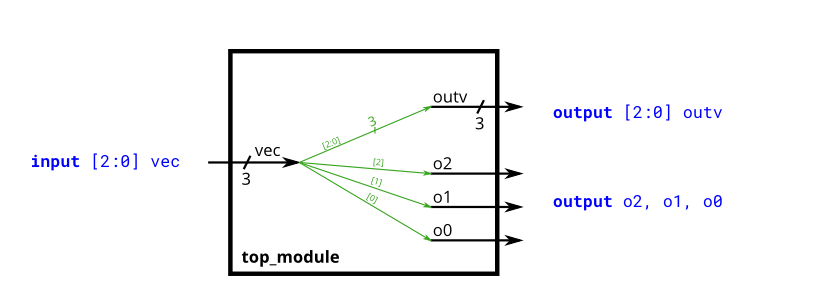
1 | module top_module ( |
Vector 1
Declaring Vectors
1 | wire [7:0] w; // 8-bit wire |
Build a combinational circuit that splits an input half-word (16 bits, [15:0] ) into lower [7:0] and upper [15:8] bytes.
Module Declaration
1 | `default_nettype none // Disable implicit nets. Reduces some types of bugs. |
1 | // Disable implicit nets. Reduces some types of bugs. |
Vector 2
A 32-bit vector can be viewed as containing 4 bytes (bits [31:24], [23:16], etc.). Build a circuit that will reverse the byte ordering of the 4-byte word.
1 | AaaaaaaaBbbbbbbbCcccccccDddddddd => DdddddddCcccccccBbbbbbbbAaaaaaaa |
This operation is often used when the endianness of a piece of data needs to be swapped, for example between little-endian x86 systems and the big-endian formats used in many Internet protocols.
1 | module top_module( |
Vectorgates
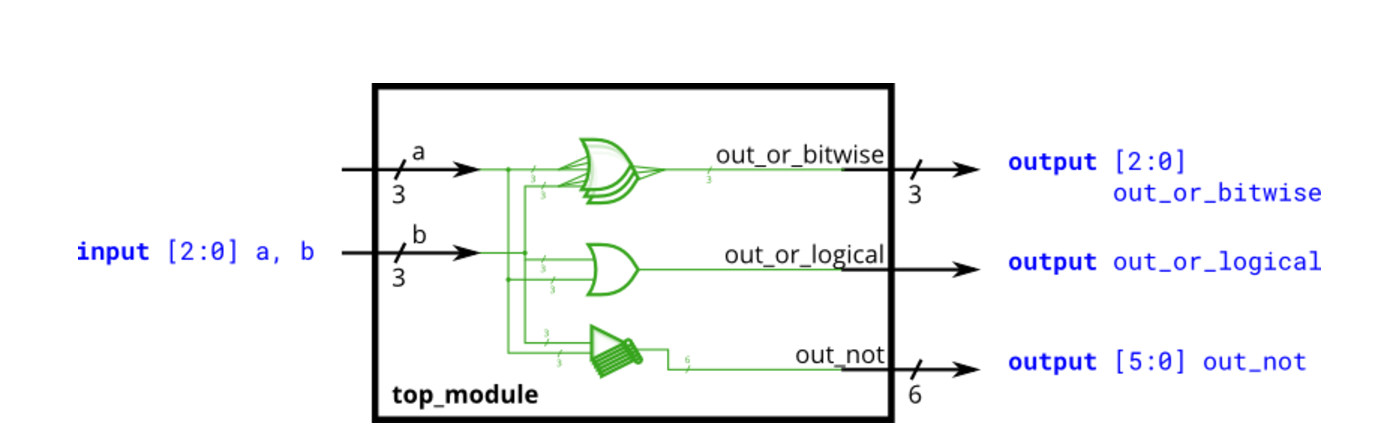
1 | module top_module( |
Gates4
1 | module top_module( |
Vector3
1 |
Modules
Procedures
Other features
All articles in this blog are licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 unless stating additionally.
Comment
