MPU6050简介 The MPU-6050 is the world’s first and only 6-axis motion tracking devices designed for the low power, low cost, and high performance requirements of smartphones, tablets and wearable sensors.
应用领域
BlurFree™ technology (for Video/Still Image Stabilization)
AirSign™ technology (for Security/Authentication)
TouchAnywhere™ technology (for “no touch” UI Application Control/Navigation)
MotionCommand™ technology (for Gesture Short-cuts)
Motion-enabled game and application framework
InstantGesture™ iG™ gesture recognition
Location based services, points of interest, and dead reckoning
Handset and portable gaming
Motion-based game controllers
3D remote controls for Internet connected DTVs and set top boxes, 3D mice
Wearable sensors for health, fitness and sports
Toys
Arduino案例 Arduino使用现成的库很容易上手。
使用Arduino进行获取数据
使用IIC进行通信
使用Wire库
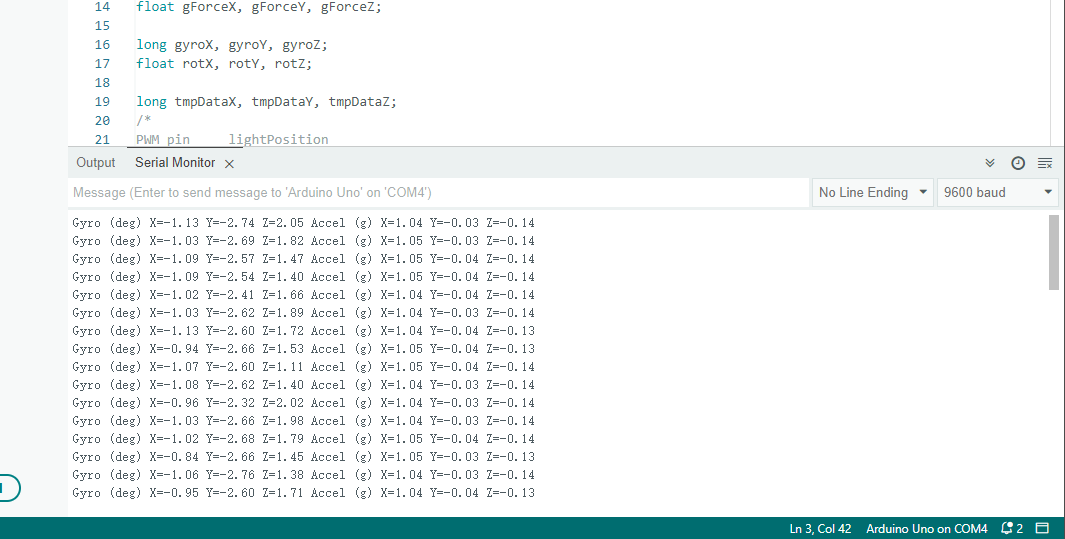
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 #include <Wire.h> const int mpuAddress= 0x68 ;long accelX, accelY, accelZ;float gForceX, gForceY, gForceZ;long gyroX, gyroY, gyroZ;float rotX, rotY, rotZ;long tmpDataX, tmpDataY, tmpDataZ;void setup () { Serial.begin(9600 ); Wire.begin(); setupMPU(); pinMode(3 , OUTPUT); pinMode(5 , OUTPUT); pinMode(6 , OUTPUT); pinMode(9 , OUTPUT); } void loop () { recordAccelRegisters(); recordGyroRegisters(); printData(); connecMPU6050WithLed(); delay(200 ); } void connecMPU6050WithLed () { if (rotX>0 ) analogWrite(3 , 255 ); else analogWrite(3 , 0 ); if (rotY>0 ) analogWrite(5 , 255 ); else analogWrite(5 , 0 ); if (rotZ>0 ) analogWrite(6 , 255 ); else analogWrite(6 , 0 ); } void testOfThefourPins () { analogWrite(3 , 255 ); analogWrite(5 , 255 ); analogWrite(6 , 255 ); analogWrite(9 , 255 ); } void setupMPU () { Wire.beginTransmission(mpuAddress); Wire.write(0x6B ); Wire.write(0b00000000 ); Wire.endTransmission(); Wire.beginTransmission(mpuAddress); Wire.write(0x1B ); Wire.write(0x00000000 ); Wire.endTransmission(); Wire.beginTransmission(mpuAddress); Wire.write(0x1C ); Wire.write(0b00000000 ); Wire.endTransmission(); } void recordAccelRegisters () { Wire.beginTransmission(mpuAddress); Wire.write(0x3B ); Wire.endTransmission(); Wire.requestFrom(mpuAddress, 6 ); while (Wire.available() < 6 ) ; accelX = Wire.read() << 8 | Wire.read(); accelY = Wire.read() << 8 | Wire.read(); accelZ = Wire.read() << 8 | Wire.read(); tmpDataX = accelX; tmpDataY = accelY; tmpDataZ = accelZ; processAccelData(); } void processAccelData () { gForceX = accelX / 16384.0 ; gForceY = accelY / 16384.0 ; gForceZ = accelZ / 16384.0 ; } void recordGyroRegisters () { Wire.beginTransmission(mpuAddress); Wire.write(0x43 ); Wire.endTransmission(); Wire.requestFrom(mpuAddress, 6 ); while (Wire.available() < 6 ) ; gyroX = Wire.read() << 8 | Wire.read(); gyroY = Wire.read() << 8 | Wire.read(); gyroZ = Wire.read() << 8 | Wire.read(); processGyroData(); } void processGyroData () { rotX = gyroX / 131.0 ; rotY = gyroY / 131.0 ; rotZ = gyroZ / 131.0 ; } void printData () { Serial.print("Gyro (deg)" ); Serial.print(" X=" ); Serial.print(rotX); Serial.print(" Y=" ); Serial.print(rotY); Serial.print(" Z=" ); Serial.print(rotZ); Serial.print(" Accel (g)" ); Serial.print(" X=" ); Serial.print(gForceX); Serial.print(" Y=" ); Serial.print(gForceY); Serial.print(" Z=" ); Serial.println(gForceZ); } void printTmpData () { Serial.print(tmpDataX); Serial.print("\t" ); Serial.print(tmpDataY); Serial.print("\t" ); Serial.print(tmpDataZ); Serial.print("\n" ); }
使用Arduino进行姿态解算
使用卡尔曼滤波进行提高数据精准度
需要进行一些数学计算
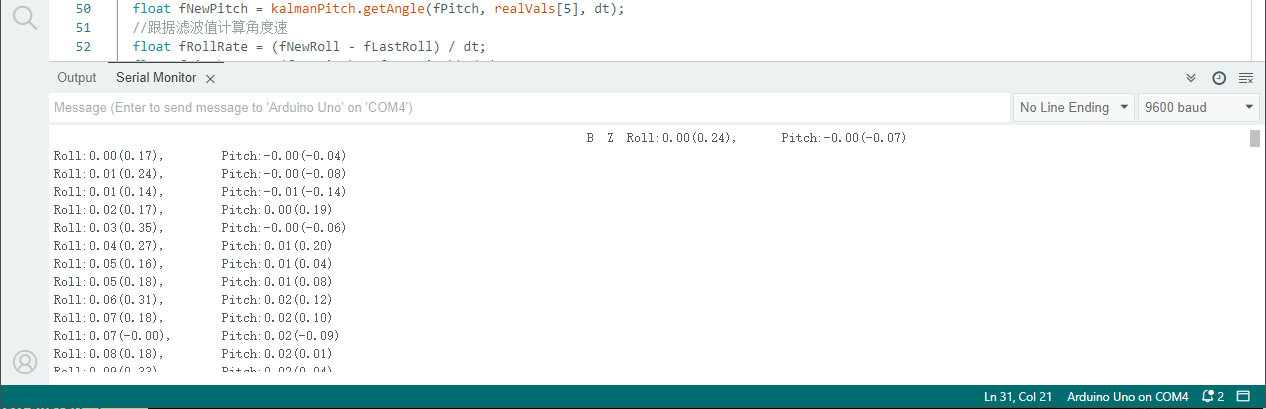
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 #include <Kalman.h> #include <Wire.h> #include <Math.h> float fRad2Deg = 57.295779513f ; const int MPU = 0x68 ; const int nValCnt = 7 ; const int nCalibTimes = 1000 ; int calibData[nValCnt]; unsigned long nLastTime = 0 ; float fLastRoll = 0.0f ; float fLastPitch = 0.0f ; Kalman kalmanRoll; Kalman kalmanPitch; void setup () { Serial.begin(9600 ); Wire.begin(); WriteMPUReg(0x6B , 0 ); Calibration(); nLastTime = micros(); } void loop () { int readouts[nValCnt]; ReadAccGyr(readouts); float realVals[7 ]; Rectify(readouts, realVals); float fNorm = sqrt (realVals[0 ] * realVals[0 ] + realVals[1 ] * realVals[1 ] + realVals[2 ] * realVals[2 ]); float fRoll = GetRoll(realVals, fNorm); if (realVals[1 ] > 0 ) { fRoll = -fRoll; } float fPitch = GetPitch(realVals, fNorm); if (realVals[0 ] < 0 ) { fPitch = -fPitch; } unsigned long nCurTime = micros(); float dt = (double )(nCurTime - nLastTime) / 1000000.0 ; float fNewRoll = kalmanRoll.getAngle(fRoll, realVals[4 ], dt); float fNewPitch = kalmanPitch.getAngle(fPitch, realVals[5 ], dt); float fRollRate = (fNewRoll - fLastRoll) / dt; float fPitchRate = (fNewPitch - fLastPitch) / dt; fLastRoll = fNewRoll; fLastPitch = fNewPitch; nLastTime = nCurTime; Serial.print("Roll:" ); Serial.print(fNewRoll); Serial.print('(' ); Serial.print(fRollRate); Serial.print("),\tPitch:" ); Serial.print(fNewPitch); Serial.print('(' ); Serial.print(fPitchRate); Serial.print(")\n" ); delay(10 ); } void WriteMPUReg (int nReg, unsigned char nVal) { Wire.beginTransmission(MPU); Wire.write(nReg); Wire.write(nVal); Wire.endTransmission(true ); } unsigned char ReadMPUReg (int nReg) { Wire.beginTransmission(MPU); Wire.write(nReg); Wire.requestFrom(MPU, 1 , true ); Wire.endTransmission(true ); return Wire.read(); } void ReadAccGyr (int *pVals) { Wire.beginTransmission(MPU); Wire.write(0x3B ); Wire.requestFrom(MPU, nValCnt * 2 , true ); Wire.endTransmission(true ); for (long i = 0 ; i < nValCnt; ++i) { pVals[i] = Wire.read() << 8 | Wire.read(); } } void Calibration () { float valSums[7 ] = {0.0f , 0.0f , 0.0f , 0.0f , 0.0f , 0.0f , 0.0 }; for (int i = 0 ; i < nCalibTimes; ++i) { int mpuVals[nValCnt]; ReadAccGyr(mpuVals); for (int j = 0 ; j < nValCnt; ++j) { valSums[j] += mpuVals[j]; } } for (int i = 0 ; i < nValCnt; ++i) { calibData[i] = int (valSums[i] / nCalibTimes); } calibData[2 ] += 16384 ; } float GetRoll (float *pRealVals, float fNorm) { float fNormXZ = sqrt (pRealVals[0 ] * pRealVals[0 ] + pRealVals[2 ] * pRealVals[2 ]); float fCos = fNormXZ / fNorm; return acos (fCos) * fRad2Deg; } float GetPitch (float *pRealVals, float fNorm) { float fNormYZ = sqrt (pRealVals[1 ] * pRealVals[1 ] + pRealVals[2 ] * pRealVals[2 ]); float fCos = fNormYZ / fNorm; return acos (fCos) * fRad2Deg; } void Rectify (int *pReadout, float *pRealVals) { for (int i = 0 ; i < 3 ; ++i) { pRealVals[i] = (float )(pReadout[i] - calibData[i]) / 16384.0f ; } pRealVals[3 ] = pReadout[3 ] / 340.0f + 36.53 ; for (int i = 4 ; i < 7 ; ++i) { pRealVals[i] = (float )(pReadout[i] - calibData[i]) / 131.0f ; } }