JAVA学习笔记 基础知识 1.String
1 2 3 String str1=“Java”;// 字符串常量值 String str3=“Java”; // 字符串常量,并且与str1地址相同 String str2=new String(“Java”);
1 2 3 4 5 str1.charAt(0); // J str1.charAt(1); // a str1.charAt(2); // v str1.charAt(4); // a str1.charAt(5); // 报错
a. 从字符串的头开始
1 2 int index = str1.indexOf('J'); System.out.println(index);// 0
b. 从下表x开始
1 2 int index1 = str1.indexOf('a',2); System.out.println(index1); //3
返回字符串出现的位置下标, 从index 开始向后 找 , 否则返回-1
1 2 3 4 5 6 public static void main (String[] args) { String s2 = "helloxawllxhxawllxh" ; int index3 = s2.lastIndexOf('a' ); System.out.println(index3); }
返回字符串出现的位置下标, 从index 开始向前 找 , 否则返回-1
1 2 3 4 5 6 public static void main(String[] args) { String s2 = "helloxawllxhxawllxh"; int index3 = s2.lastIndexOf('xawl'); System.out.println(index3);//12 }
截取后面的字符串内容
1 2 3 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { String str = "adsasdasdasdasd"; String ret = str.substring(4);// 保留第4个 System.out.println(ret);//sdasdasdasd }
截取指定部分
1 2 3 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { String str = "adsasdasdasdasd"; String ret = str.substring(4,7);//截取[4,7)里面的字符 System.out.println(ret);//sda }
使用replace或者replaceAll
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 public static void main (String[] args) { String str1 = "xawlxawlxawlxawl" ; String ret = str1.replace("xa" ,"B" ); String ret1 = str1.replaceAll("xa" ,"B" ); System.out.println(ret); System.out.println(ret1); System.out.println(str1); }
使用split方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 public static void main(String[] args) { String str1 = "Hello this is xawl rjgc professional"; String[] ret = str1.split(" "); //以空格为分隔符,拆分整个字符串为多个字符串 for (String s : ret) { System.out.println(s); } } /******************************************************/ public static void main(String[] args) { String str1 = "Hello this is xawl rjgc professional"; String[] ret = str1.split(" ",3); //以空格为分隔符,拆分3个字符串 for (String s : ret) { System.out.println(s); } }
注意 特殊字符(| + * . ,)作为分割符可能无法正确切分, 需要加上转义.
1 2 3 4 5 6 public static void main(String[] args) { String str = String.valueOf(1234); String str1 = String.valueOf(12.34); System.out.println(str); System.out.println(str1); }
小写字母转大写字母或者相反 toUpperCase() &toLowerCase()
1 2 3 4 5 6 public static void main(String[] args) { String str3 = "abcdef阿凡达"; String ret = str3.toUpperCase(); System.out.println(ret);//ABCDEF阿凡达 }
2. 数组
1 2 //数组的长度 int Alength=a.length;
//转化为String
1 2 3 //转化为String String str=Arrays.tString(array);
数组拷贝和扩容
1 int[] tmp = Arrays.copyOf(array,2*array.length);
Arrays.binarySearch
1 2 3 //查找成功的话会返回数据的位置 int index = Arrays.binarySearch(arr, 55);
Arrays.equals(比较两个数组是否相等)
1 2 3 Arrays.equals(int[] a, int [] b); //当且仅当a.b非空,长度相同,元素相同时返回true
Arrays.fill(填充;一般用于初始化)
Arrays.sort(arr)
3.数据类型转换
byte<short<char<int<long<float<double
1 2 3 4 int num_1=20 ;byte num_2=(byte ) a;int num_3=300 ;byte num_4=(byte )num_3;
4. Java 中super的用法 当子类的构造方法内第一行没有出现“super()”时,系统会默认给它加上无参数的”super()”方法 。
注意:
当子类构造方法的第一行执行super()无参数方法,那么父类中一定要有无参数构造方法。
在一个类中写了有参数的构造方法时,无参数构造方法就会不存在,需要自己补上无参数的构造方法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 class father { public int age; public father () {} public father (int a) {this .age=age;} } class son extends father { public son () { super (5 ); } }
Java 中 final 的用法
1)final 修饰变量,表示变量的值不可改变,此时该变量可被称为常量。
2)final 修饰方法,表示方法不能被子类重写;
重写:子类中如果创建了一个与父类中相同名称、相同返回值类型、相同参数列表的方法,只是方法体中的实现不同,以实现不同于父类的功能,这种方式被称为方法重写,又称为方法覆盖。
3)final 用在类的前面表示该类不能有子类,即该类不可以被继承。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 public static final String NAME = "regen" ;NAME = new String ("regen" ); class User { public final String getName () { return "user:" 张三"; } } class Reader extends User{ @Override public final String getName(){ return " 李四"; //compilation error: overridden method is final } } //final修饰类 //例如 java 中的String类 //表示该类 具有完整的功能,不能被继承 public final class String implements java.io.Serializable, Comparable<String>, CharSequence { /** The value is used for character storage. */ private final char value[]; ... }
final 关键字,提高了性能,JVM 和 Java 应用都会缓存 final 变量。
final 变量,可以安全的在多线程环境下进行共享,而不需要额外的同步开销。
Java面向对象
java bean
提供一个默认的无参构造函数。
需要被序列化并且实现了 Serializable 接口。
可能有一系列可读写属性,并且一般是 private 的。
可能有一系列的 getter 或 setter 方法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 public class People { privete String name; private int age; public void setName (String newName) { name = newName; } public String getName () { return name; } public void setAge (int neweAge) { age = newAge; } public int getAge () { return age; } }
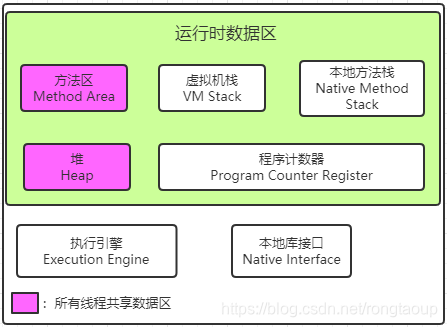
1.JVM内存结构 * 对象的存储结构
对象应该看作一个地址
对象名指向堆中的首地址(swap 案例)
基本数据类型比较的是数值,而引用数据类型比较的是内存地址
堆、栈、方法区、程序计数器
程序技计数器一个线程独享的数据区域,也就是说,每个线程之间的数据相互不干扰,是一个线程内存空间。
可以当成字节码的行号指示器
JVM的栈包括Java虚拟机栈 和本地方法栈
Java虚拟机栈:执行Java方法服务。
本地方法栈: 执行JVM使用到的Native方法服务。
natine 方法是什么?
JDK 中有很多方法是使用 Native 修饰的。Native 方法不是以 Java 语言实现的,而是以本地语言实现的(比如 C 或 C++)
栈是线程私有的,每个线程拥有独立的栈空间
栈的元素为栈帧
特点:
1. 是Java虚拟机管理内存中的最大一块区域。
1. 被所有线程共享。
1. 用来存放用 new 创建过的对象
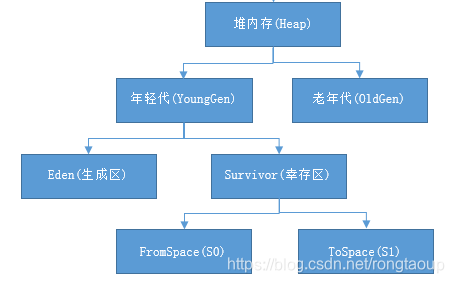
堆内存的分类
特点:
被所有线程共享
存储已被虚拟机加载的类信息、常量、静态变量、即时编译器编译后的代码。
包含了常量池
常量池:
常量池避免了频繁的创建和销毁对象而影响系统性能,其实现了对象的共享。
2. 包 1.命名规则
统一使用小写
单数形式
使用 . 分隔开
一般是网站的反写形式
包的权限 * public 共有
* protected
3. 多态 1.多态的转型
1 2 父类类型 引用名 = new 子类类型(); //右侧创建一个子类对象,把它当作父类看待使用
只能强制转换父类的引用,不能强制转换父类的对象 要求父类的引用必须指向的是当前目标类型的对象
1 2 子类类型 引用名 = (子类类型) 父类引用; //用强制类型转换的格式,将父类引用类型转为子类引用类型
可以利用操作符instanceof 判断是否类型一致或为子类型(返回boolean类型)
2. 动态绑定
当调用对象方法 的时候,该方法会和该对象的运行类型 绑定
当调用对象属性 时,没有动态绑定 机制,即哪里声明,哪里使用。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 package dynamic_;public class DynamicBinding { public static void main (String[] args) { Person p1 = new Student (); p1.mission(); } } class Person { public void mission () { System.out.println("人要好好活着!" ); } } class Student extends Person { @Override public void mission () { System.out.println("学生要好好学习!" ); } }
3. 多态参数 多态参数 :方法定义的形参类型 为父类 类型,实参类型 允许为子类 类型。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 package polyparameter;public class PolyParameter { public static void main (String[] args) { Student s1 = new Student ("小蓝同学" ); Teacher t1 = new Teacher ("小绿老师" ); PolyParameter polyParameter = new PolyParameter (); polyParameter.test(s1); polyParameter.test(t1); } public void test (Person p) { if (p instanceof Student){ ((Student) p).study(); } else if (p instanceof Teacher){ ((Teacher) p).teach(); } } } class Person { private String name; public Person (String name) { this .name = name; } public String getName () { return name; } public void setName (String name) { this .name = name; } } class Student extends Person { public Student (String name) { super (name); } public void study () { System.out.println(super .getName() + "\t" + "正在好好学习" ); } } class Teacher extends Person { public Teacher (String name) { super (name); } public void teach () { System.out.println(super .getName() + "\t" + "正在好好教书" ); } }
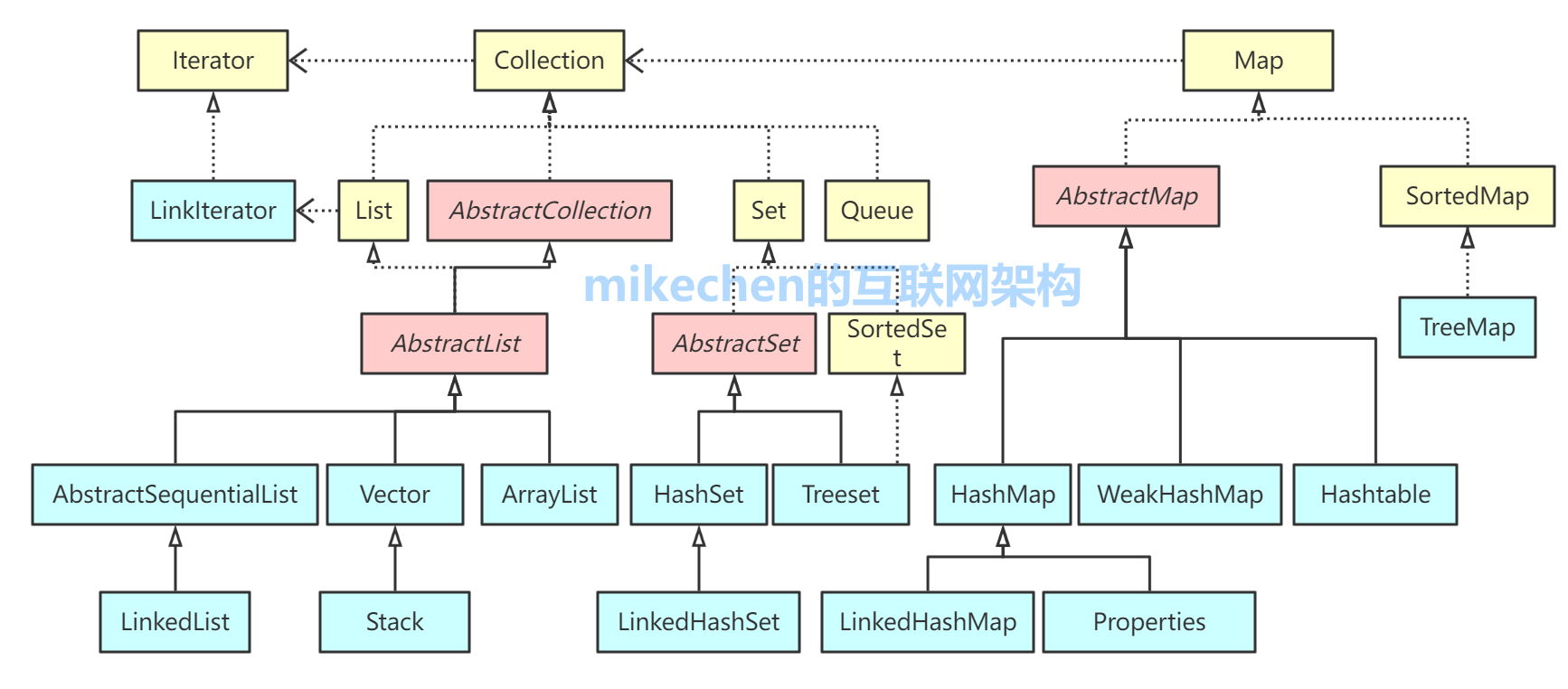
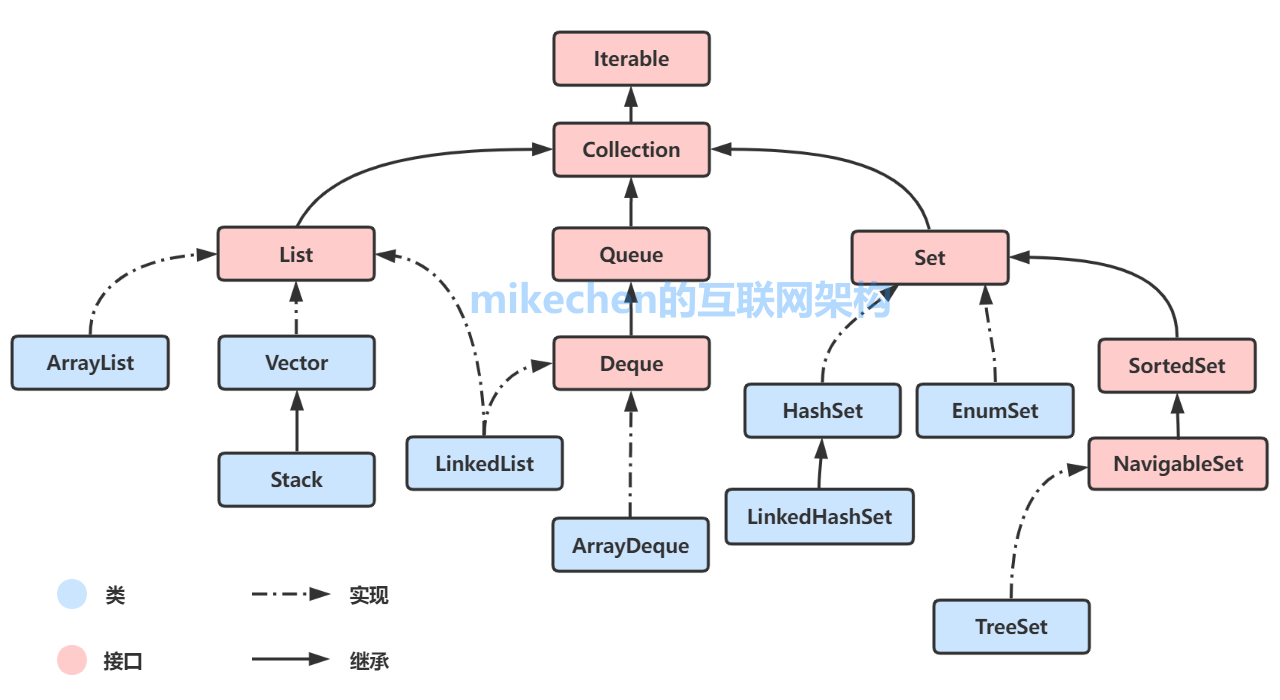
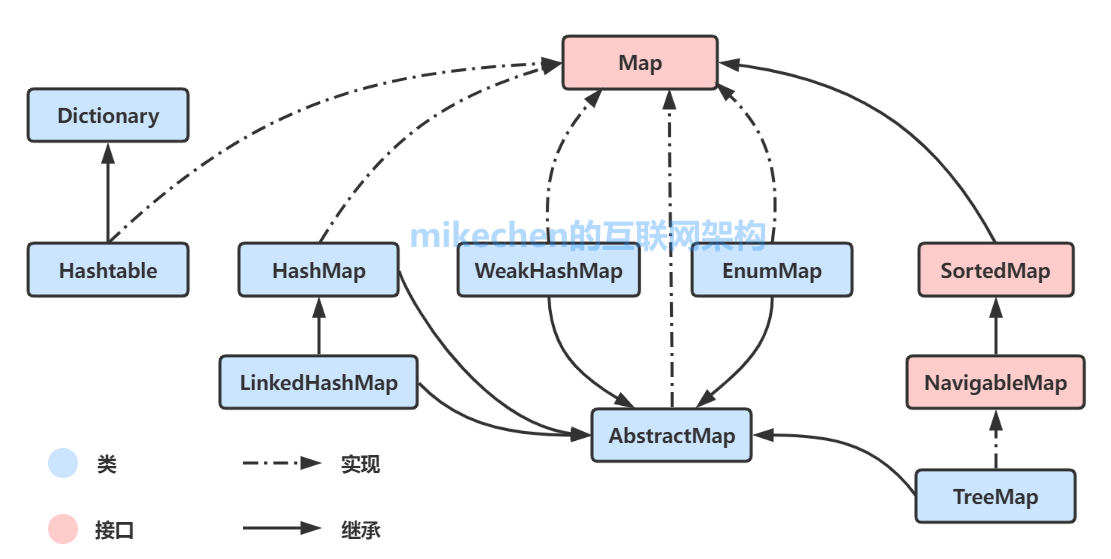
Java集成体系框架 整体框架:
Java集合类主要由两个根接口Collection和Map派生出来。
1. Collection
1.增删查改
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 ArrayList<Object> arrl =new ArrayList<>(); //增 arr1.add( E e ); //删 remove(Object o) //从该集合中删除指定元素的单个实例 clear() //从此集合中删除所有元素 //查 arr1.getI(int index); //获取第 i 个数,从零开始 //改 set(int index, E element) //用指定的元素替换此列表中指定位置的元素。
2. 迭代器
1 2 arr1.iterator() //返回一个集合的迭代器 arr1.toArray() //转数组
常见方法
2. Map
抽象类和接口 抽象类(abstract class ) 接口。 Java不允许多重继承,但是接口可以实现多重继承,即一个类可以实现多个接口。
JDBC
定义:JDBC(Java DataBase Connectivity:java数据库连接)是一种用于执行SQL语句的Java API,可以为多种关系型数据库提供统一访问,它是由一组用Java语言编写的类和接口组成的。
简单使用过程
导入jar包
注意:使用与MySQL版本适配的jar包,使用与操作系统一致的jar包
案例程序(链接云数据库):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 import java.sql.Connection;import java.sql.DriverManager;import java.sql.ResultSet;import java.sql.SQLException;import java.sql.Statement;public class main { static final String JDBC_DRIVER = "com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver" ; static final String DB_URL = "jdbc:mysql://142.171.33.151:3306/mydata" ; static final String USER = "root" ; static final String PASS = "123456" ; public static void main (String[] args) { Connection conn = null ; Statement stmt = null ; try { Class.forName(JDBC_DRIVER); System.out.println("connecting" ); conn = DriverManager.getConnection(DB_URL,USER,PASS); stmt = conn.createStatement(); String sql; sql = "SELECT * FROM emp" ; ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql); while (rs.next()){ System.out.println( rs.getInt("id" ) +"\t" + rs.getString("name" )+"\t" ); } rs.close(); stmt.close(); conn.close(); }catch (SQLException se){ se.printStackTrace(); }catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); }finally { try { if (stmt!=null ) stmt.close(); }catch (SQLException se2){ } try { if (conn!=null ) conn.close(); }catch (SQLException se){ se.printStackTrace(); } } System.out.println("Goodbye!" ); } }